I have seen many trading concepts and tools over the years become popular and then fade away, from indicators and strategies to software for finding profitable trades. They all seem to be trying to view the markets in a new way and promise something we haven’t seen before. However, supply-and-demand trading has been around for more than a century. It is a concept that will continue to exist for many years because it lies at the foundation of price movements, unlike indicators or other tools derived from price.
This article will not tell you everything you need to know about supply-and-demand trading, because the topic is too big. Rather, I want to give you the main principles and help you begin your journey of using supply and demand in your trading.
Top Regulated Brokers
What Is Supply and Demand in Forex?
Supply relates to sellers, and demand to buyers. When demand exceeds supply, prices rise, and when supply exceeds demand, prices fall.
The concept of “supply and demand” in Forex refers to the imbalance between the two, and that imbalance is the catalyst for price moves. I think of supply and demand as an X-ray of the market, revealing the imbalance between buyers and sellers. That’s what makes it such a powerful tool.
Understanding supply and demand is a core concept for all Forex trading styles because it allows retail traders to align with institutional order flow, i.e., where large market participants are most active.
The co-founder of one of the world’s most successful traditional proprietary trading firms, Mike Bellafiore from SMB Capital, recently said: “Mastering supply and demand in trading is one of the most important skills you can learn as a trader, and failing to learn it can be a disaster.”
Supply and demand analysis is not specific to a single timeframe. It applies to both short-term and long-term charts.
Supply and Demand Zones Explained
Supply and demand zones are areas on a chart where strong buying or selling causes prices to move sharply away from that level. These zones represent areas where large market participants, in other words, institutions, placed orders. Many times, those large institutional orders did not get filled.
A supply zone forms when selling pushes the price down, while a demand zone forms when strong buying drives the price up. When the price returns to a supply or demand zone, it often reacts again because the remaining orders may still be there.
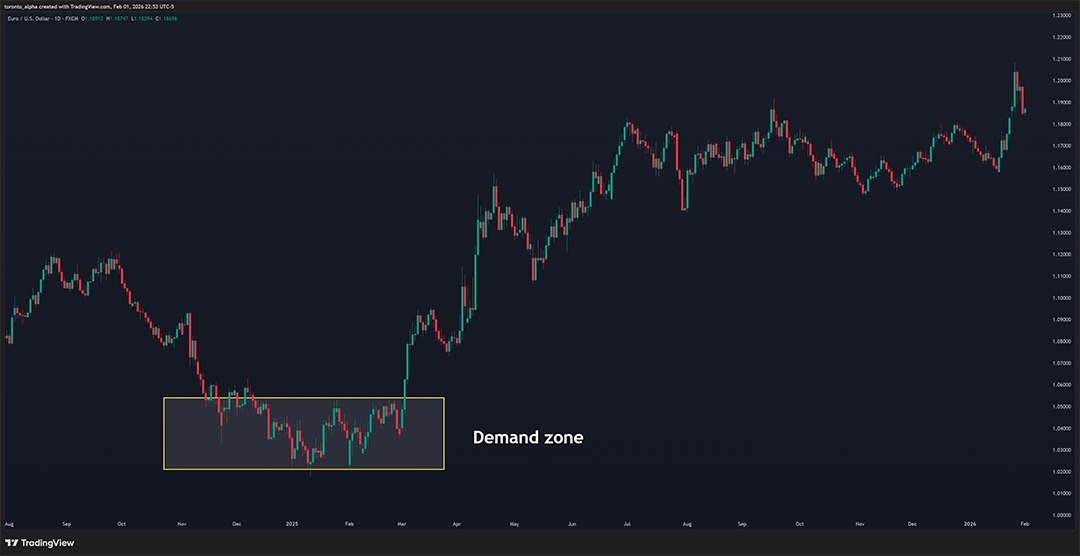
In the above chart, the price moves into an area and stalls. There’s a battle between buyers and sellers, and eventually, the buyers prevail, and the price moves sharply out of that zone.
How to Identify Supply and Demand Zones on Forex Charts
Key Price Action Clues
The best supply-and-demand zones are when the price moves rapidly away from a consolidation or range. Look for candlesticks patterns that have long candles with small wicks, showing a rapid departure from the area. This type of move indicates a significant imbalance between buyers and sellers.
Some traders specifically look for three consecutive full-bodied candles in the same direction.
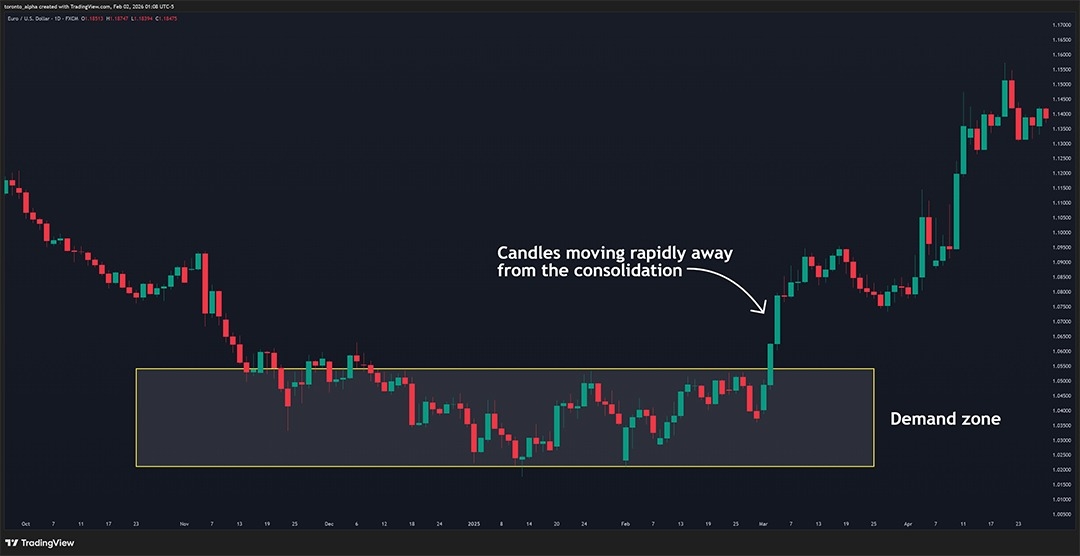
When trying to find the most recent supply or demand zone, go to the current price on the right edge of the chart, and trace the price back until you find the origin of that move. That will often take you to the most recent zone. I find this technique useful for beginners to practice finding zones.
Timeframes and Zone Strength
A common theme in technical analysis is that higher time frames will prevail over lower ones, and that’s true for supply and demand analysis. Timeframes such as the daily and 4-hour charts generally produce stronger supply and demand zones than lower timeframes, such as the 15-minute chart.
Remember, higher timeframes capture more volume and activity and better reflect institutional activity. Institutions have much larger position sizes and can spend days or weeks getting in and out of their positions, thereby creating zones on the larger timeframes.
Of course, the definition of a high timeframe is relative to everyone’s trading style. A scalper that executes on the 1-minute chart might use the 1-hour chart as their higher timeframe.
Therefore, begin supply and demand analysis by finding zones on higher timeframes, and use lower timeframes to plan entries and exits in line with the bigger picture.
Tools That Help
Volume Profile: This is one of my favourite tools to use with supply and demand. Volume Profile shows volume at different price levels. It conceptually aligns with Supply and Demand because it also helps confirm institutional activity across different price levels, making it a mutually beneficial tool.
Wyckoff Method: A more specialized method of interpreting Supply and Demand. The Wyckoff Method, developed by Richard Wyckoff in the early 1900s, provides a framework for markets by dividing them into four distinct phases: Accumulation, Markup, Distribution, and Markdown. Wyckoff is such a popular method within supply and d1emand analysis that many people use the terms interchangeably.
Basic Supply and Demand Forex Trading Strategies
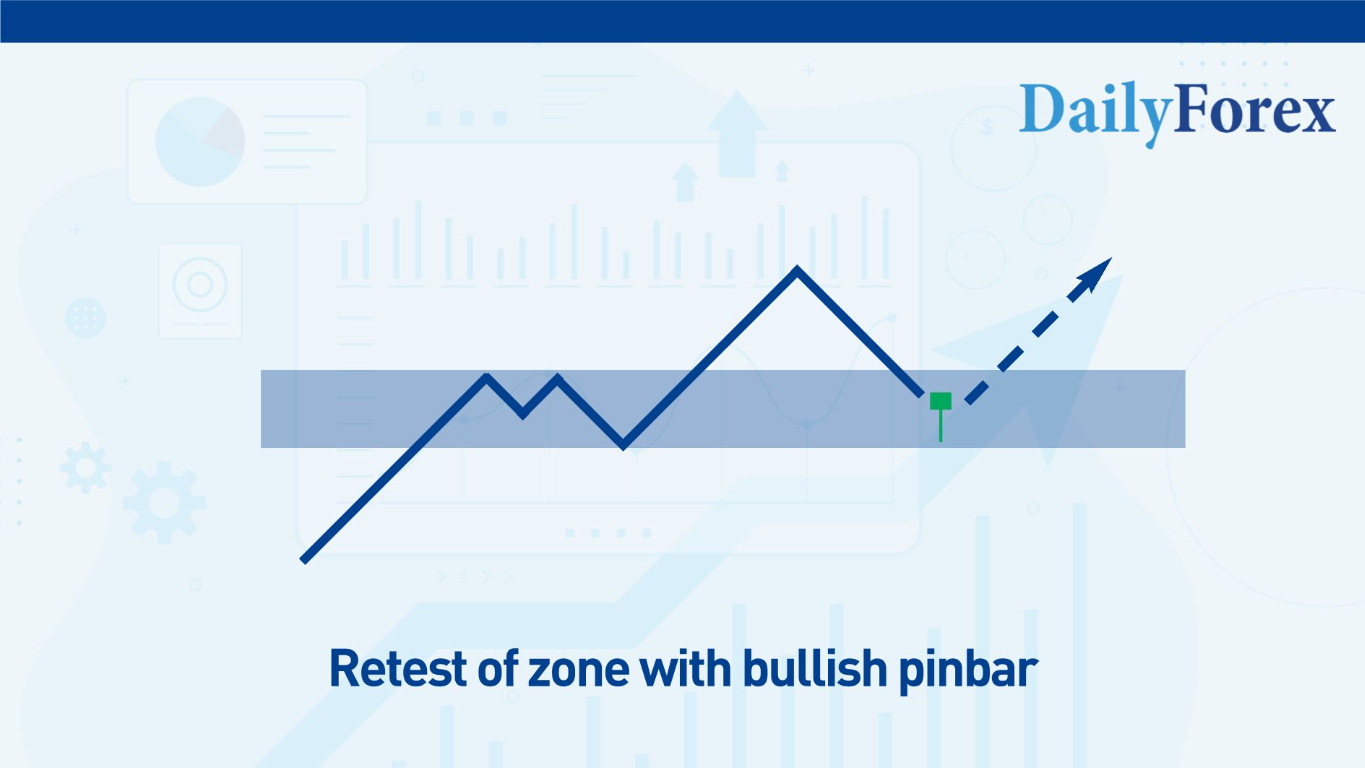
Bounce (Reversal) Trades from Zones
A bounce trade is when the price returns to a supply or demand zone and shows signs of rejection. For example, if the price returns to a previous demand zone, a trader could look for the price to stall at that level or to make bullish candlestick setups, such as a Bullish Pinbar or a Bullish Engulfing pattern.
A common method is to place stop-losses just beyond the zone, with targets aimed at the next zone in the opposite direction.

Breakout and Retest Trades
When price breaks cleanly through a supply or demand zone, it often means that market activity has absorbed the imbalance. However, instead of jumping into a potentially false breakout, it’s often better to wait until the price comes back to retest and bounce off that level in the direction of the breakout. This can lead to safer trades and help keep stop losses tighter, resulting in better reward/risk ratios. However, sometimes it means missing the move if the price continues in the breakout direction without retesting the level.
Combining Zones with Trend Direction
The best piece of advice I could give any trader is to trade with the overall trend, particularly trends on the higher timeframes. Sometimes I’ve made sloppy entries on lower timeframes, but the bigger trend has still carried me into profit.
In a big uptrend, focus on finding demand zones at lower timeframes; in a big downtrend, focus on finding supply zones. This methodology will lead to improved consistency and lower stress trading.
Common Mistakes in Supply and Demand Forex Trading
Drawing too many zones: High-quality zones are created by strong, clear moves—not minor fluctuations. My chart shouldn’t be crowded with zones—it’s confusing and leads to overtrading. If I am having to spend a lot of effort deciding whether a zone is valid, it probably isn’t. A strong zone should be immediately clear to me. I once heard a trader say that a child should be able to see the clear levels on a chart, and I think that’s good advice.
Ignoring market context: Markets do not operate in a vacuum. Big trends and news affect how the price moves. Take into account the bigger market structure and context to get the best out of supply-and-demand trading.
Practical Tips to Improve Your Supply and Demand Trading
- Start by knowing the bigger trend before marking zones.
- Focus on quality, clear zones. Trading well-defined zones, even if fewer in number, will outperform trading multiple minor zones at weak levels.
- Take time to practice supply-and-demand on demo accounts or through backtesting.
- Always consider risk management in your trading. I recommend the following: only trade money you can afford to lose; never risk more than a specified percentage of your account size on each trade; always use a stop-loss; and take trades with good reward-to-risk ratios.
Conclusion
Supply-and-demand Forex trading is foundational to understanding how markets move. By learning how to mark the zones, retail traders can trade in line with larger market participants, especially institutions. This can give better entries and better reward/ratios on trade. Like all trading methods, Supply-and-demand trading should take into account higher timeframes, larger trends, significant news announcements, and market context. Supply-and-demand trading takes practice, but it’s worth the time investment.
