For luxury and aesthetic appeal, gold is arguably the most popular metal. In the financial sector, it has almost equal relevance. The gold market is a $22 trillion sector according to market data at the time of writing.
Gold has enjoyed success as a store of value, with a reputation as a safe-haven asset built over centuries. However, it continues to be limited by its sheer nature. These limits are related to custody and the ease of investing in and spending gold. For context, a ‘good delivery’ bar of gold weighs about 12 kg and is worth at least $80,000.
Gold tokenization attempts to improve the flexibility of gold and simplify gold custody, investments, and spending. Gold tokenization is the process of creating a representation of real gold on the blockchain. Gold tokenization projects use smart contract technology to create tokens that are pegged to the value of a measure of real gold.
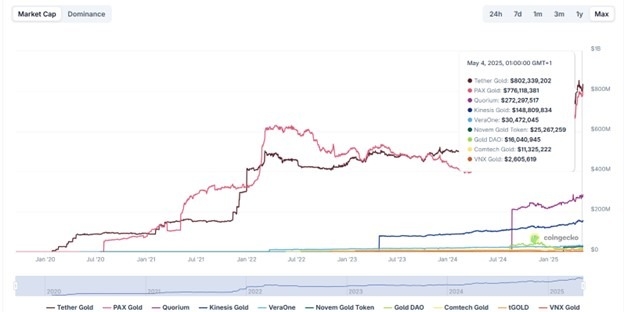
Coingecko
The total market cap of tokenized gold sits at over $2 billion at the time of writing, according to data from Coingecko.
How Gold Tokenization Works
Here is a step-by-step guide detailing how tokenization of gold works:
Acquisition and Custody: First, the project issuing the gold tokens acquires real gold and stores it in a safe storage facility like the Swiss Gold Vault.
Minting of Gold Tokens: The issuer mints a defined number of tokens on a smart contract blockchain like the Ethereum, Tron, or Solana networks. The nature of the token may vary depending on the blockchain on which it is issued. For instance, ERC20 on Ethereum and TRC20 on Tron blockchain.
Pegging Structure: The minted tokens are pegged to a measure of gold, like the Troy ounce or Gram. The total market cap of minted tokens is expected to correspond to the equivalent value of the actual gold in the issuer’s custody.
Distribution and Auditing: The minted gold is distributed to investors and listed on the supporting crypto exchanges. Gold tokens can be spent like any other crypto asset. The issuer is expected to develop an auditing system like Proof of Reserves (POR) that enables investors to verify that they hold an equivalent amount of real gold.
Minting and Redemption: On request, gold token holders can redeem their tokens for an equivalent amount of real gold. When a gold token is redeemed, the issuer burns the gold token. When anyone who holds real gold wishes to tokenize their gold or if the issuer acquires more real gold, new gold tokens will be minted.
Top Regulated Brokers
Gold Tokenization – Pros and Cons
Pros
Gold tokenization offers numerous advantages, including:
Low barrier to entry: Gold tokenization opens access to this asset class. It allows anyone to explore investment opportunities in the gold market.
Fractionalization: The tokenization of gold enables investors to purchase a fraction of a unit of gold. Gold tokens can be split into up to ten decimal places.
Flexibility and cost-efficient transaction: Tokenized gold is held in cryptocurrency wallets. Compared to real gold, they are easier to store and spend.
Transaction costs for tokenized gold are also significantly lower than the cost to transfer real gold.
Passive income: Tokenized gold can be used to earn passive income on DeFi platforms through liquidity and yield farming programs.
Cons
Gold tokenization also faces some challenges, like:
Unclear regulatory framework: The regulatory structure for gold tokenization is still developing. Stringent regulations may negatively impact existing gold token projects and limit mass adoption.
Custody issues: Tokenized gold issuers might mismanage the tokenization system and the real gold that backs the tokens. This could lead to significant losses for holders.
Volatility: Like other crypto assets, tokenized gold may face more volatility than real gold. This is due to lower liquidity and the structure of the crypto market.
Use Cases
Use cases of tokenized gold include:
P2P transaction: Tokenized gold can be used to settle routine financial agreements. Like Bitcoin, gold token holders can easily send tokens to their friends and any merchants that accept them.
Store of value: The value of gold and tokenized gold has grown in the past five years. Like real gold, tokenized gold is a viable store of value.
DeFi Application: Tokenized gold can be traded on decentralized exchanges, used to borrow or lend on DeFi lending platforms, or used to farm yield.
Examples of Tokenized Gold
Tether Gold (XAUT): XAUT is issued by Tether and is pegged to one Troy ounce of gold. It can be purchased on OKX, Bybit, and Whitebit exchanges.
Paxos Gold (PAXG): PAXG is issued by Paxos and regulated by the New York State Department of Financial Services (NYDFS). It is pegged to one troy ounce of gold and can be traded on Binance, Kraken, and MEXC exchange.
Kinesis Gold (KAU): KAU is issued by Kinesis and pegged to a gram of gold. It can be traded on Bitmart, Emirex, and Kinesis Money.
Comtech Gold (CGO): CGO is a gold token pegged to one gram of gold. It is issued by ComTech and can be traded on LBank, Bitmart, and Bitrue.
Bottom Line
Tokenized gold expands access to the gold market and allows for easy gold custody, transactions, and management. Tokenized gold can also be integrated into emerging financial technologies like DeFi and re-staking. In both scenarios, it enables gold investors to explore more value for their investments. Despite the regulatory bottlenecks in gold tokenization, the idea has enjoyed significant growth and could improve to meet investors' demand and grow in terms of mass adoption.
Having said this, it is worth noting that gold tokenization is an emerging concept and is vulnerable to significant changes in the future. Cryptocurrency investments are risky, so always do your own research before investing in tokenized gold. This article does not endorse any featured project.
Ready to trade gold with confidence? Explore our gold trading strategies and market insights here.

